
Remember that the length of economic upswings between recessions has become longer in the U.S. Most economists, even those who are concerned about a possible pattern of persistently large budget deficits, are much less concerned or even quite supportive of larger budget deficits in the short run of a few years during and immediately after a severe recession.Ī glance back at economic history provides a second illustration of the power of automatic stabilizers.

The Great Recession, starting in late 2007, meant less tax-generating economic activity, which triggered the automatic stabilizers that reduce taxes. In addition, the automatic stabilizers react to a weakening of aggregate demand with expansionary fiscal policy and react to a strengthening of aggregate demand with contractionary fiscal policy, just as the AD/AS analysis suggests.Ī combination of automatic stabilizers and discretionary fiscal policy produced the very large budget deficit in 2009.

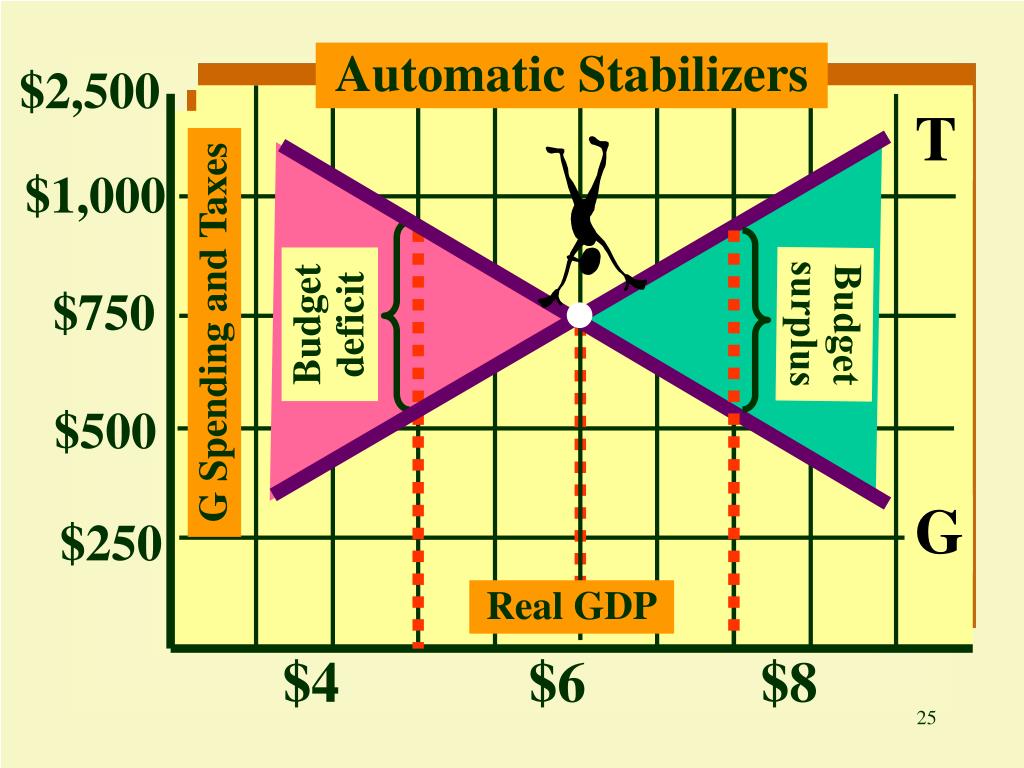
In 2009, the stimulus package included an extension in the time allowed to collect unemployment insurance. Higher unemployment and a weaker economy should lead to increased government spending on unemployment benefits, welfare, and other similar domestic programs. The lower level of aggregate demand and higher unemployment will tend to pull down personal incomes and corporate profits, an effect that will reduce the amount of taxes owed automatically. If aggregate demand were to fall sharply so that a recession occurs, then the prescription would be for expansionary fiscal policy-some mix of tax cuts and spending increases. On the spending side, stronger aggregate demand typically means lower unemployment and fewer layoffs, and so there is less need for government spending on unemployment benefits, welfare, Medicaid, and other programs in the social safety net. Because taxes are based on personal income and corporate profits, a rise in aggregate demand automatically increases tax payments. On the tax side, a rise in aggregate demand means that workers and firms throughout the economy earn more. To some extent, both changes happen automatically. The policy prescription in this setting would be a dose of contractionary fiscal policy, implemented through some combination of higher taxes and lower spending. This situation will increase inflationary pressure in the economy. Counterbalancing Recession and BoomĬonsider first the situation where aggregate demand has risen sharply, causing the equilibrium to occur at a level of output above potential GDP. Changes in tax and spending levels can also occur automatically, due to automatic stabilizers, such as unemployment insurance and food stamps, which are programs that are already laws that stimulate aggregate demand in a recession and hold down aggregate demand in a potentially inflationary boom. Federal fiscal policies include discretionary fiscal policy, when the government passes a new law that explicitly changes tax or spending levels.

The millions of unemployed in 2008–2009 could collect unemployment insurance benefits to replace some of their salaries.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
